As is known, osteochondrosis is a chronic pathology caused by degenerative changes in the structure of the spine. Unfortunately, 8 out of 10 people among the adult population suffer from osteochondrosis.
Pathology can begin at a young age (20-25 years), gradually becoming complicated by new manifestations. In general, lumbar, thoracic and cervical osteochondrosis are distinguished.
Disease symptoms
Osteochondrotic lesions of the cervical spine are characterized by:
- Dull pain in the neck and back of the head (cervicalgia);
- If the vertebral artery is damaged, then the activity of the nerve center responsible for normalizing pressure indicators is disturbed, so hypertension is often an accompanying pathology of osteochondrosis;
- During the development of cervical osteochondrosis, spinal artery compression occurs, which causes the occurrence of symptoms such as extraneous sounds in the ears, dizziness and visual disturbances, paroxysmal headaches;
- Heart pain radiates to the shoulder blades and neck, just like the pain of angina pectoris.
Lumbar osteochondrosis is characterized by symptoms:
- Severe pain due to compression of the spinal cord root, as well as the venous-arterial highway that delivers nutrition to the spinal cord;
- When the lower lumbar root is affected, the disease is accompanied by shooting pain along the outside of the leg, which turns into a decrease in the sensitivity of this area;
- Often, lumbar osteochondrosis is manifested by shooting pain from the lower back to the legs, then this symptom is replaced by a decrease in sensitivity in the lower legs;
- With the development of complications in the form of intervertebral hernia, manifestations such as weakness in the legs, lumbar pain, decreased muscle tone and leg sensitivity, and leg muscle weakness (paresis) occur.
Manifestations of thoracic osteochondrosis:
- With upper lesions, pain is observed in the abdomen, chest, shoulders and scapula;
- Lower lesions are accompanied by a decrease in the sensitivity of the lower thoracic vertebrae, accompanied by pelvic organ dysfunction. When moving or sneezing, the pain increases;
- In rare cases, thoracic osteochondrosis causes spinal compression, which is characterized by local girdling pain radiating to the intercostal space, abdomen, groin or lower leg, weakness and numbness in the legs, and disturbances in the activity of the pelvic organs.

Treatment options
In the treatment of osteochondrosis, various therapeutic techniques are used:
- Drug therapy;
- Physiotherapy (massage procedures, physical therapy, etc. );
- Diet therapy;
- Corrective therapy;
- Ethnoscience;
- Surgery.
How to treat cervical, thoracic and lumbar osteochondrosis at home
Each method of anti-osteochondrosis therapy aims to relieve pain with subsequent elimination, normalize the course of vertebral structural processes and restore the activity of the radicular spine.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy for osteochondrosis is based on several areas:
- Symptomatic therapy aims to eliminate pain and involves taking anti-inflammatory drugs. Along with anti-inflammatory drugs, patients are prescribed muscle relaxants from the group of muscle relaxants;
- Treatment aimed at normalizing blood circulation involves the use of vasodilators;
- Cartilage tissue restoration therapy is based on the use of chondroprotective drugs;
- Vitamin therapy is based on the intake of complex vitamins;
- Treatment with antidepressants is used to relieve anxiety and depressive states, which often occur in patients with a background of limited movement and pain of osteochondrosis origin.
- Therapy with herbal preparations often helps significantly alleviate the patient's condition, as such drugs restore immune defenses, sleep and body strength, and prevent depression.
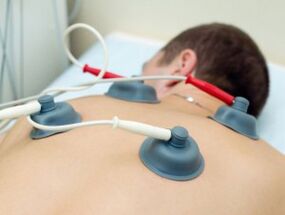
Physiotherapy activities
Sufficiently effective in the fight against osteochondrosis are physiotherapeutic measures that:
- Helps in eliminating pain syndrome;
- Increase the amplitude of the motor ability;
- Improving and facilitating the course of the immune process;
- Normalizes blood circulation;
- Normalize metabolic processes;
- Provide a reduction in the therapeutic dose of non-steroidal drugs and anti-inflammatory analgesics.
Physiotherapy has many types. In the treatment of anti-osteochondrosis the following are most often used:
- Electrotherapy involves carrying out procedures related to the influence of electric current, such as electrophoresis, galvanization, electrosleep, darsonvalization and others using special devices;
- Shock wave therapy is carried out with a device that converts electrical impulses into ultrasound waves, which, acting on the spine affected by osteochondrosis, accelerates the healing of damaged bone tissue and cartilage, relieves pain and swelling;
- Balneotherapy involves the use of mineral water and mud, after exposure to improved blood supply, pain is eliminated and substance metabolism is normalized;
- Magnetotherapy - this device is based on the use of a constant magnetic field created by a special inductor placed in the affected vertebral area;
- Laser therapy is based on the use of a special laser, which, by acting on the affected tissues, contributes to their recovery.
All physiotherapeutic methods provide symptomatic treatment of osteochondrosis, relieve inflammation and pain, reduce the course of treatment and the dose of medication taken.
Diet
Since anti-osteochondrosis therapy is complex, it requires a rationally balanced diet.
For patients with this disease, it is very important to limit the intake of liquids, salt, and simple carbohydrates. They need to be removed from the diet:
- Alcohol;
- Beverages such as cocoa, coffee, and strong tea;
- Pickles and spicy dishes;
- Products that are too rich in extractives (mushrooms, fatty fish, chicken, meat, etc. ).
Since osteochondrosis causes the destruction of intervertebral cartilage, their recovery requires animal protein, which is rich in dairy products, lean fish or meat.
Meat or jelly soup prepared from the boiled bones of beef or pig's feet is very useful for such patients. This broth is rich in collagen, which provides bones and cartilage tissue with additional strength.

Exercise that improves health
Therapeutic exercise plays an equally important role in the treatment of osteochondrosis; moreover, it is considered the most effective method to combat the destruction of bone and cartilage cells, helps to strengthen muscles and joint tissue, ensures mobility of the spine and helps in the recovery of damaged tissue.
When doing physical therapy exercises, some simple conditions should be observed:
- Movement should not cause severe pain attacks or any discomfort, if such effects occur, it is necessary to discuss the situation with a doctor;
- You should not exercise during the period of exacerbation of the disease, otherwise the symptoms of pain may increase or complications may develop;
- You need to do the exercise smoothly, avoiding sudden movements.
The necessary set of exercises is selected by the doctor according to the patient's condition and the level of development of osteochondrosis.
massage
The massage procedure helps improve blood circulation and has a relaxing effect on the patient's muscles. The massage starts with light strokes, then continues to rubbing and kneading. Massage can be done with your hands or using a special object such as a jar.
Cupping massage for osteochondrosis helps to relieve muscle tension and activate metabolic processes in the affected tissue due to better blood flow and lymph flow. Acupressure, which involves influencing active spinal points, has no less therapeutic effect.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine, which has many recipes for various rubs and compresses, can also help in the treatment of osteochondrosis. Thanks to folk remedies that increase blood flow, it is possible to relieve pain and relax muscles.
This tool is based on:
- Essential oils (fir, etc. );
- melted lard;
- Camphor alcohol;
- Badger fat;
- honey;
- Bee venom, snake;
- Medicinal roots and herbs such as aloe, birch or radish leaves, garlic, ginger, red pepper.
They are combined with alcohol, iodine, and turpentine, which results in a local irritant effect. Mustard baths (200 grams of powder per water bath) are excellent for sudden acute pain relief.

Orthopedic accessories
A good addition to home treatment for osteochondrosis is the use of orthopedic accessories that ensure complete relaxation of the spine during night rest.
Therefore, while sleeping, you need to take the correct and comfortable body position.
High-quality mattresses and orthopedic pillows can help with this. Thanks to the use of such a device, the spine will be completely relaxed at night, which will eliminate the symptoms and improve the patient's condition.
Osteochondrosis can be treated independently, the main thing is to observe the regularity, consistency, complexity of the procedure and coordinate all actions with a specialist.



















